Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card
Fault caused by contact oxidation due to leakage of heat conduction pad
The liquid leaked from the heat conduction pad not only causes harmless pollution to the graphics card, but also may cause short circuit due to the adhered conductive dirt and the deterioration of the conductivity of the oxidation area of the leaked material. When the card is normally installed in the drill, the liquid mainly flows to the video card contact inserted in the riser. The problem occurs because the motherboard cannot detect the video card and freezes during the PCI-E equipment detection phase. BIOS。 Sometimes due to poor contact, code 43 errors occur, and the operating system often crashes after loading, even if there is no overclocking, and temperature detection errors occur.
Usually, this kind of failure is caused by the use of poor heat conduction pad (gray) and the high temperature (over 70 ℃) during the operation of the graphics card.
In this case, check whether the test point on the video card board is short circuited, the resistance is normal, and the BIOS of the video card is normal. The contacts of the connector are covered with oxide and have corrosion traces.
In this case, troubleshooting includes cleaning/restoring the contacts. The contacts can be cleaned with alcohol (medical or isopropyl alcohol), Kalosha gasoline.
To prevent such failures, please do not operate the video card at a temperature higher than 65 ℃; For preventive cleaning, please replace the dry gray heat conduction pad with a better one.
Search for an open circuit on the fuse in the video card power circuit
Normally, the resistance of the fuse should be about zero ohms. Check them by measuring the resistance between the contacts with an ohmmeter.
Fuses in the 12 volt power supply circuit on the PCI Express line:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 1.
The resistance between the right/left contacts of this fuse and pins 1, 2, and 3 of the PCI-E connector (12 volt power supply from the motherboard/riser) should also be equal to zero:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 2.
Fuses near the power connector of Sapphire AMD RX580 Nitro Plus series video card:
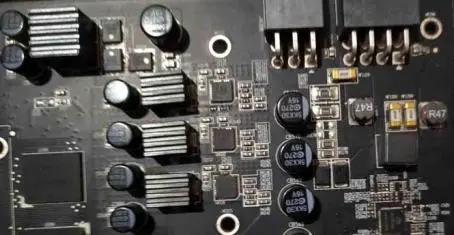
Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 3.
A graphics card with a power connector usually has two fuses (for example, the RX470 Nitro has two fuses for a 12 V power supply):
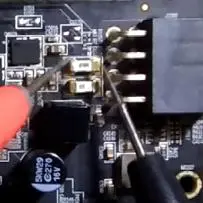
Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 4.
Usually these are 10 amp fuses, which can be easily replaced by similar ones.
If the fuse is found to be blown and replaced, do not rush to open the card. First, you need to figure out what caused it to fail.
Failure caused by failure of electronic components of video card
Most failures of electronic equipment and any other electrical engineering are caused by lack of necessary or unnecessary/parasitic contact (short circuit). In this case, the most dangerous situation is the breakdown of some components, resulting in a short circuit, which usually leads to a large number of electronic components and circuit board components burned. During the visual inspection of the circuit board of the faulty video card, such faults can be identified visually.
If burnt components cannot be found visually, use an ohmmeter (tester in resistance measurement mode) to locate the problem.
With the tester, you need to measure the resistance of the fuse (it should be about zero ohms), whether there is a short circuit and the circuit interruption between the video card quality (ground, usually a “minus sign”) and the control point.
During the control check, the black wire of the equipment is connected to the ground and the red wire is connected to the positive pole of the circuit under test. The resistance must be:
On the video card chip – a few (1-2) ohms;
On video memory and video memory controller – tens of ohms;
On the power line of PCI-E controller – tens of ohms;
The resistance of the PCI-E power cord is 3.3 volts – hundreds of ohms/kiloohms.
If there is a short circuit or open circuit at a certain time, the fault is in the circuit.
When a short circuit is detected, the test is usually carried out by applying a low voltage with limited current from the laboratory power supply to identify the heating failure component. The working chip should normally be heated moderately. The components of the power system should also normally be cold.
Example of measuring resistance on AMD Radeon RX series video card Resistance measurement of power phase MOSFET
The MOSFET of the power supply system shall not have short circuit or open circuit. The 12 volt (Vin) contact on the graphics card power supply MOSFET must be checked for a short circuit. To do this, you need to know where to supply 12 volts to them.
For example, according to the pin arrangement of IR3553 mosfet commonly used in AMD Radeon RX series video cards, the Vin power supply voltage pin is on the right:
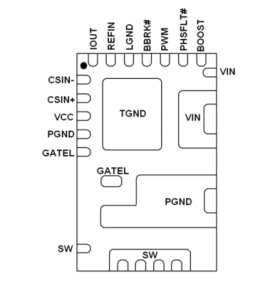
Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 5.
Example of checking the resistance between Vin and ground on the power supply phase of IR3553 mosfet of AMD Radeon RX470:
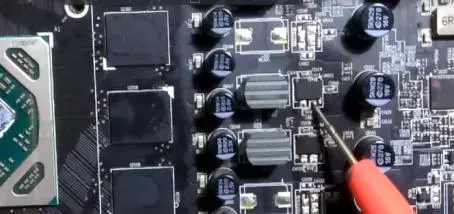
Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 6.
Therefore, you need to check each MOSFET of the power supply phase and replace it if a short circuit is detected.
Check the resistance of MOSFET in the power supply circuit of AMD Radeon RX580 series video card:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 7.
Resistance between the power supply phase choke of the RX580 (1.86 kOhm) and+12 volts:
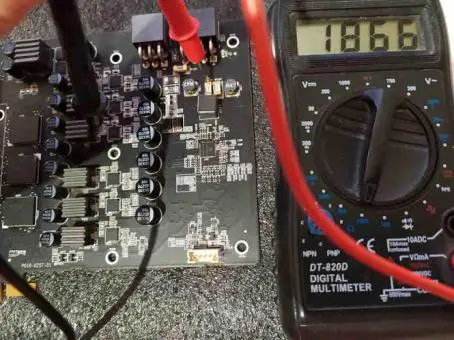
Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 8.
When welding the faulty element, the resistance should return to normal. If this is not the case, you need to continue to look for the components that cause the short circuit (usually these are punched electrolytic capacitors).
Check the resistance of the PCI-E power line
The resistance on the PCI-E controller wire should be about 10-20 ohms:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 9.
Measure the resistance of the supply line PCI-E 3.3 volts
The resistance along the PCI-E 3.3 volt power cord (the eighth pin on the PCI-E connector) should be in the order of hundreds of ohms or kiloohms:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 10.
Resistance measurement of video card chip
The resistance of the card chip should be several ohms.
Example of measuring the chip resistance on the Sapphire Radeon RX 480 Nitro Plus power supply phase choke (six of them, 1.6-1.7 ohms each):

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 11.
Check the resistance of Sapphire Radeon RX 480 Nitro graphics card chip:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 12.
Check the resistance in the power supply circuit of the video memory controller
The resistance at the PLL inductance in the power supply circuit of the video memory controller shall be 10-60 ohms:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 13.
Choke of power circuit of video memory controller on the other side of video card (AMD Radeon RX580 Nitro Plus with 4 GB video memory):
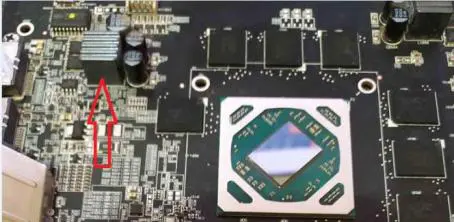
Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 14.
The resistance on the memory controller of the RX470 graphics card is 53 ohms:
Resistance measurement of video memory power supply
Choke and pipe of memory power supply phase of RX580 graphics card:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 15.
Video memory power supply stage of RX470 video card:
The power supply resistance of RX graphics card memory is usually tens of ohms:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 16.
Same pin on RX580 board:

Typical Fault Diagnosis of AMD Radeon RX Video Card Figure 17.